 From Spiral06 To Spiral07
From Spiral06 To Spiral07
The code for the Model Concepts project is at model_concepts on GitHub.
The code for the Magic Boxes project is at mb_spirals on GitHub. For teaching or learning purposes, each spiral in Magic Boxes is decomposed into several sub-spirals.
In Spiral 06, a line tool in the tool bar, allows a line creation between the last two clicked boxes.
In Spiral 07, a line may be selected and deleted. A menu bar has Edit, View and Create menus. The Edit menu has menu items for selecting all boxes and lines, and for deleting selected boxes and lines. The View menu has menu items for hiding and showing selected boxes and lines. The Create menu has menu items for generating boxes in a diagonal and as tiles.
The MenuBar class has a new content with six buttons.
Code 06-07.01: The MenuBar class with six buttons.
class MenuBar {
final Board board;
// Edit
ButtonElement selectAllButton;
ButtonElement deleteSelectionButton;
// View
ButtonElement hideSelectionButton;
ButtonElement showHiddenSelectionButton;
// Create
ButtonElement createBoxesInDiagonalButton;
ButtonElement createBoxesAsTilesButton;
MenuBar(this.board) {
selectAllButton = document.querySelector('#select-all');
deleteSelectionButton = document.querySelector('#delete-selection');
hideSelectionButton = document.querySelector('#hide-selection');
showHiddenSelectionButton = document.querySelector('#show-hidden-selection');
createBoxesInDiagonalButton = document.querySelector('#create-boxes-in-diagonal');
createBoxesAsTilesButton = document.querySelector('#create-boxes-as-tiles');
// Menu bar events.
selectAllButton.onClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
board.select();
});
deleteSelectionButton.onClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
board.deleteSelection();
});
hideSelectionButton.onClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
board.hideSelection();
});
showHiddenSelectionButton.onClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
board.showHiddenSelection();
});
createBoxesInDiagonalButton.onClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
board.createBoxesInDiagonal();
});
createBoxesAsTilesButton.onClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
board.createBoxesAsTiles();
});
}
}The Board class has changed to provide methods used in the MenuBar class. The select method select boxes only. The line selection will be done in one of the next steps towards the Spiral 07.
Code 06-07.02: The select method of the Board class.
void select() {
selectBoxes();
}Similarly, the deleteSelection, hideSelection and showHiddenSelection methods do not yet handle selected lines.
Code 06-07.03: The deleteSelection method of the Board class.
void deleteSelection() {
deleteSelectedBoxes();
}
void hideSelection() {
hideSelectedBoxes();
}
void showHiddenSelection() {
showHiddenBoxes();
}The createBoxesInDiagonal method of the Board class generates boxes in a diagonal (Figure 06-07.01). The initialization of the x and y local variables is done in a single line of code. The while loop may seem to iterate forever, because its condition to loop is true. However, the false condition of the if statement enters the else part and the return statement stops the iterations by exiting the method. If the next box may be positioned diagonally within the board, the box is created in that position. The x and y variables are incremented by the two constants from the Box class before the next iteration.
Code 06-07.04: Boxes created in a diagonal.
void createBoxesInDiagonal() {
int x = 0; int y = 0;
while (true) {
if (x <= width - Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH && y <= height - Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT) {
Box box = new Box(this, x, y, Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH, Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
boxes.add(box);
x = x + Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH;
y = y + Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT;
} else {
return;
}
}
}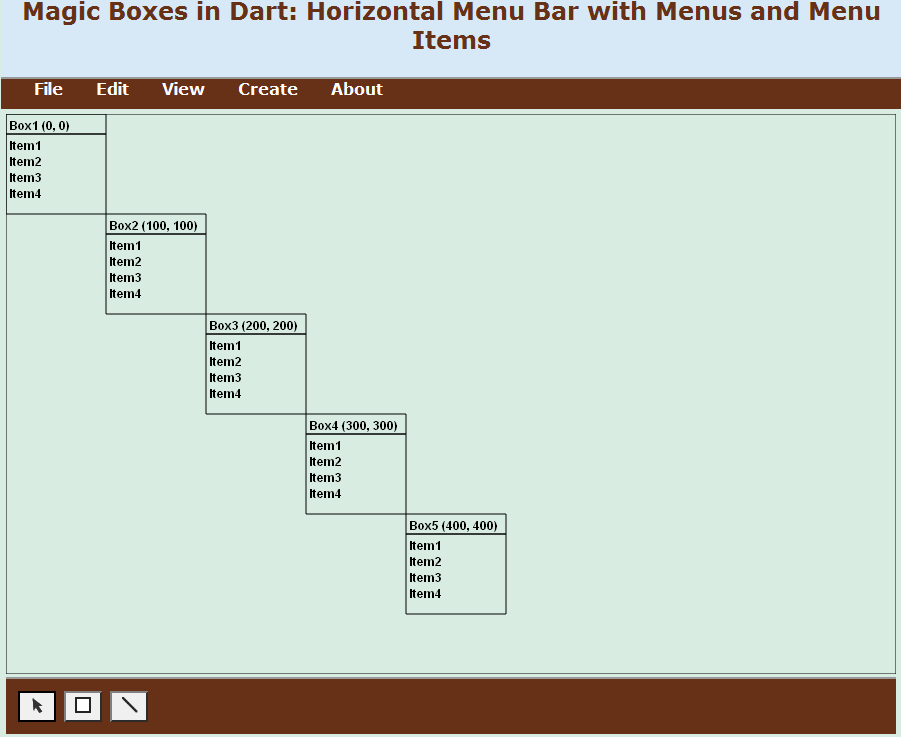
Figure 06-07.01: Five boxes created in a diagonal.
The createBoxesAsTiles method of the Board class generates boxes as tiles (Figure 06-07.02). If a new box may be positioned as a tile within the board, the box is created in that position. It is a value of the y variable that determines when the method will be returned to a caller.
Code 06-07.05: Boxes created as tiles.
void createBoxesAsTiles() {
int x = 0; int y = 0;
while (true) {
if (x <= width - Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH) {
Box box = new Box(this, x, y, Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH, Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
boxes.add(box);
x = x + Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH * 2;
} else {
x = 0;
y = y + Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT * 2;
if (y > height - Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT) {
return;
}
}
}
}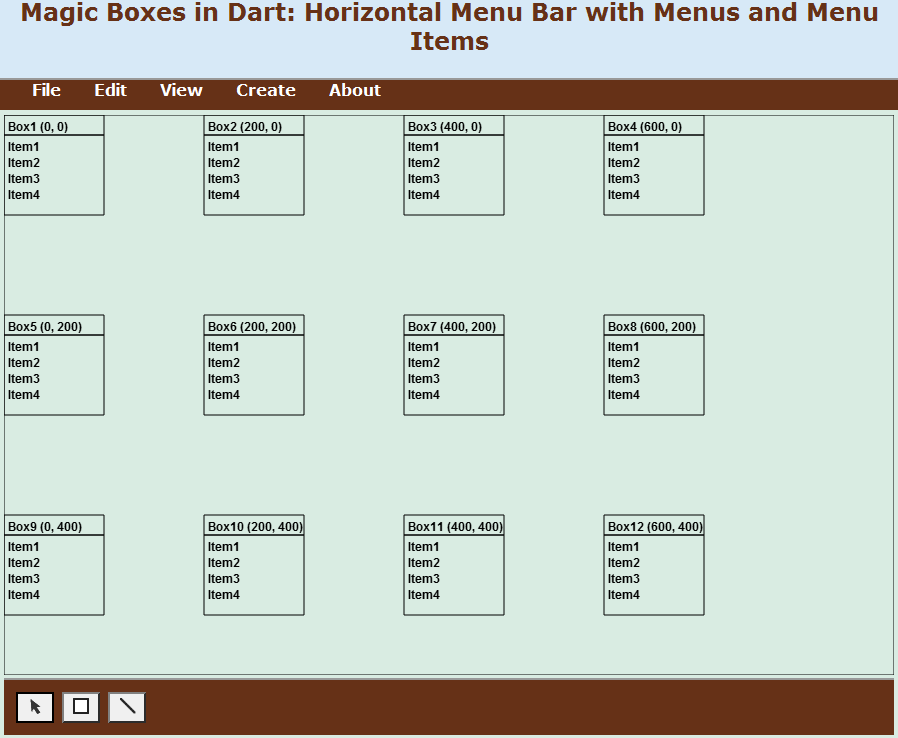
Figure 06-07.02: Twelve boxes created as tiles.
The nav element of HTML5 contains an unordered list of items that are menus. Each menu contains another unordered list of items that are menu items.
Code 06-07.06: The navigation section of HTML5.
<nav>
<ul>
<li>File
<ul>
<li></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Edit
<ul>
<li>
<button id="select-all">
Select All
</button>
</li>
<li>
<button id="delete-selection">
Delete Selection
</button>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>View
<ul>
<li>
<button id="hide-selection">
Hide Selection
</button>
</li>
<li>
<button id="show-hidden-selection">
Show Selection
</button>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Create
<ul>
<li>
<button id="create-boxes-in-diagonal">
Boxes in Diagonal
</button>
</li>
<li>
<button id="create-boxes-as-tiles">
Boxes As Tiles
</button>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>About
<ul>
<li>Magic Boxes in
<a href="http://www.dart.org/">Dart</a>
</li>
<li>Spiral 07</li>
<li>2011-12-23</li>
<li>Dzenan Ridjanovic</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>The menu.css file has selectors that present the navigation section of the mb.html file as a menu bar with menus and drop down menu items.
Code 06-07.07: CSS presentation of drop down menus.
nav {
width: 100%;
height: 30px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #ffffff;
background-color: #663117;
border-top: 2px solid #999999;
}
nav ul {
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
nav ul li {
display: inline;
height: 30px;
float: left;
list-style: none;
margin-left: 15px;
position: relative;
}
nav ul li:hover {
color: #d9ece2;
}
nav li ul {
margin: 0px;
padding-top: 8px;
display: none;
position: absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 20px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #d9ece2;
background-color: #663117;
}
nav li:hover ul {
display: block;
width: 180px;
}
nav li li {
padding: 0px;
color: #ffffff;
list-style: none;
display: list-item;
}
nav li li a:link {
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: #e6ffc8;
}
nav li li a:visited {
text-decoration: none;
font-weight: bold;
color: #f2e1fb;
}
nav li li a:hover {
text-decoration: none;
color: #663117;
background: #d9ece2;
}
nav li li button {
color: #663117;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: bold;
background-color: #ffffff;
}
nav li li button:hover {
background-color: #d9ece2;
}Lines may be selected (Figure 06-07.03) and then hidden. The Line class two private attributes initialized both to false to state that a new line is neither selected nor hidden. In the constructor of the Line class, a default line width is borrowed from the context attribute of the board.
Code 06-07.08: New attributes in the Line class.
bool _selected = false;
bool _hidden = false;
num defaultLineWidth;
Line(this.board, this.box1, this.box2) {
defaultLineWidth = board.context.lineWidth;
draw();
}The line selection appears in the title of the Web page.
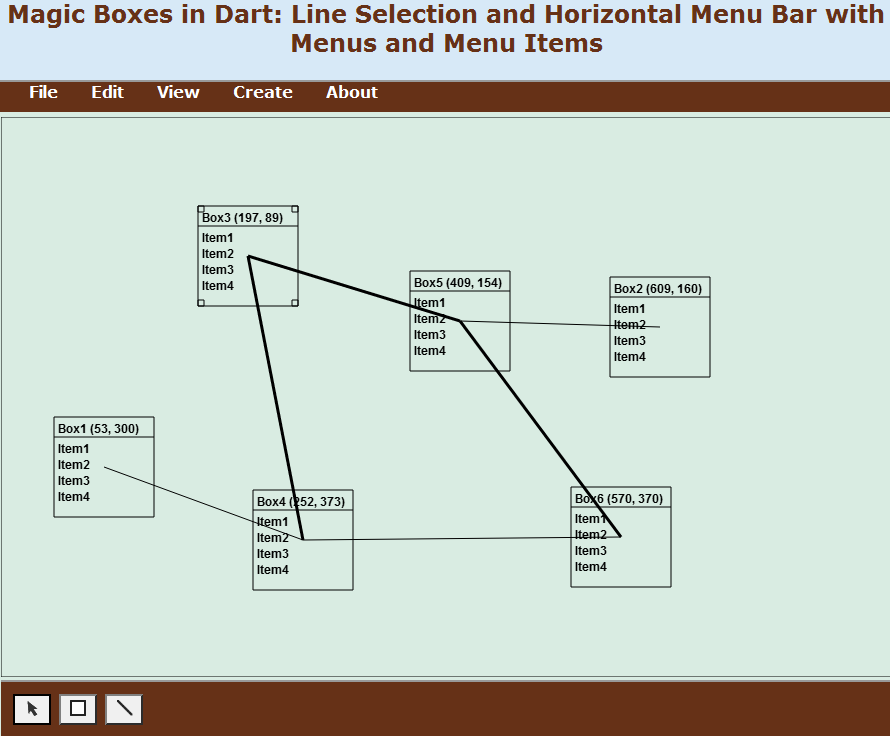
Figure 06-07.03: Selected lines have a bigger width.
The draw method of the Line class draws a line if it is not hidden. The width of a selected line is bigger for 2 pixels than the default width.
Code 06-07.09: The draw method of the Line class.
void draw() {
if (!isHidden()) {
board.context.beginPath();
board.context.moveTo(box1.x + box1.width / 2,
box1.y + box1.height / 2);
board.context.lineTo(box2.x + box2.width / 2,
box2.y + box2.height / 2);
if (isSelected()) {
board.context.setLineWidth(defaultLineWidth + 2);
} else {
board.context.setLineWidth(defaultLineWidth);
}
board.context.closePath();
board.context.stroke();
}
}The methods for the two private attributes are expressed in short notation.
Code 06-07.10: Short notation used in select, hide and their related methods.
select() => _selected = true;
deselect() => _selected = false;
toggleSelection() => _selected = !_selected;
bool isSelected() => _selected;
hide() => _hidden = true;
show() => _hidden = false;
bool isHidden() => _hidden;The contains method of the Line class returns true if the given point is on the line between the centers of the two boxes with the error of delta in pixels. The method uses the Point class of Dart.
Code 06-07.11: The contains method of the Line class.
bool contains(Point point, Point delta) {
if (box1.contains(point.x, point.y) || box2.contains(point.x, point.y)) {
return false;
}
Point pointDif = new Point(0, 0);
bool inLineRectX, inLineRectY, inLineRect;
double coord;
Point beginPoint = box1.center();
Point endPoint = box2.center();
pointDif.x = endPoint.x - beginPoint.x;
pointDif.y = endPoint.y - beginPoint.y;
// Rapid test: Verify if the point is in the line rectangle.
if (pointDif.x > 0) {
inLineRectX = (point.x >= (beginPoint.x - delta.x)) &&
(point.x <= (endPoint.x + delta.x));
} else {
inLineRectX = (point.x >= (endPoint.x - delta.x)) &&
(point.x <= (beginPoint.x + delta.x));
}
if (pointDif.y > 0) {
inLineRectY = (point.y >= (beginPoint.y - delta.y)) &&
(point.y <= (endPoint.y + delta.y));
} else {
inLineRectY = (point.y >= (endPoint.y - delta.y)) &&
(point.y <= (beginPoint.y + delta.y));
}
inLineRect = inLineRectX && inLineRectY;
if (!inLineRect) {
return false;
}
// If the line is horizontal or vertical there is no need to continue.
if ((pointDif.x == 0) || (pointDif.y == 0)) {
return true;
}
if (pointDif.x.abs() > pointDif.y.abs()) {
coord = beginPoint.y +
(((point.x - beginPoint.x) * pointDif.y) / pointDif.x) - point.y;
return coord.abs() <= delta.y;
} else {
coord = beginPoint.x +
(((point.y - beginPoint.y) * pointDif.x) / pointDif.y) - point.x;
return coord.abs() <= delta.x;
}
}There are many additions and changes in the Board class to support different actions on lines.
Code 06-07.12: Methods on lines in the Board class.
void deleteLines() {
lines.clear();
}
void deleteSelectedLines() {
lines.removeWhere((l) => l.isSelected());
}
void deleteSelection() {
deleteSelectedLines();
deleteSelectedBoxes();
}
void selectLines() {
for (Line line in lines) {
line.select();
}
}
void select() {
selectBoxes();
selectLines();
}
void deselectLines() {
for (Line line in lines) {
line.deselect();
}
}
void deselect() {
deselectBoxes();
deselectLines();
}
void hideSelectedLines() {
for (Line line in lines) {
if (line.isSelected()) {
line.hide();
}
}
}
void hideSelection() {
hideSelectedBoxes();
hideSelectedLines();
}
void showHiddenLines() {
for (Line line in lines) {
if (line.isHidden()) {
line.show();
}
}
}
void showHiddenSelection() {
showHiddenBoxes();
showHiddenLines();
}
int countSelectedLines() {
int count = 0;
for (Line line in lines) {
if (line.isSelected()) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
int countSelectedLinesContain(int pointX, int pointY) {
Point delta = new Point(DELTA, DELTA);
int count = 0;
for (Line line in lines) {
if (line.isSelected()
&& line.contains(new Point(pointX, pointY), delta)) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
Line _lineContains(Point point) {
Point delta = new Point(DELTA, DELTA);
for (Line line in lines) {
if (line.contains(point, delta)) {
return line;
}
}
}The DELTA constant of the Board class has the value of 8 pixels. This means that within the 8 pixels surrounding a line, a click will select the line. The private lineContains method of the Board class returns a line that contains the given point with the DELTA error.
In the onMouseMethod of the Board class, if a click happens outside of an existing box and the select tool is on, the click point is passed to the private lineContains method. If the method returns a line, the toggleSelection method is applied to the line. Otherwise, selected boxes and lines are deselected.
Code 06-07.13: The active select tool part of the onMouseDown method.
void onMouseDown(MouseEvent e) {
…
if (!clickedOnBox) {
if (toolBar.isSelectToolOn()) {
Point clickedPoint = new Point(e.offset.x, e.offset.y);
Line line = _lineContains(clickedPoint);
if (line != null) {
// Select or deselect the existing line.
line.toggleSelection();
} else {
// Deselect all.
deselect();
}
} …
}The draw method of the Box class must use the default line width in order draw the current box properly. Without the setLineWidth method, after a line is selected, the boxes may have the same line width as the selected line.
Code 06-07.14: The defaultLineWidth attribute of the Box class.
num defaultLineWidth;
Box(this.board, this.x, this.y, this.width, this.height) {
titleNo = board.nextBoxNo;
defaultLineWidth = board.context.lineWidth;
draw();
…
}
void draw() {
if (!isHidden()) {
board.context.beginPath();
…
board.context.lineWidth = defaultLineWidth;
board.context.closePath();
board.context.stroke();
}
}The Board class has also the defaultLineWidth attribute that is used in drawing a border.
Code 06-07.15: The defaultLineWidth attribute of the Board class.
num defaultLineWidth;
Board(CanvasElement canvas) {
…
defaultLineWidth = context.lineWidth;
border();
…
}The defaultLineWidth attribute is used in drawing the diagram border.
Code 06-07.16: The border has the default width.
void border() {
context.beginPath();
context.rect(0, 0, width, height);
context.lineWidth = defaultLineWidth;
context.closePath();
context.stroke();
}When deleting a selected box, if the box is one of the last two clicked boxes referenced by the lastBoxClicked attribute or the beforeLastBoxClicked attribute, the corresponding attribute must reference null instead of the deleted box. Otherwise, a new line may be created that is hanging in the air.
Code 06-07.17: Nullifying one of the last two clicked boxes.
void deleteSelectedBoxes() {
for (Box box in boxes.toList()) {
if (box.isSelected()) {
boxes.remove(box);
if (box == beforeLastBoxClicked) {
beforeLastBoxClicked == null;
} else if (box == lastBoxClicked) {
lastBoxClicked == null;
}
}
}
}The delete method of the Board class must delete all lines and boxes and the fixed tool should return to select.
Code 06-07.18: The delete method of the Board class.
void delete() {
deleteLines();
deleteBoxes();
toolBar.backToSelectAsFixedTool();
}The private selectToolDblClicked attribute of the bool type is replaced by the private fixedTool attribute of the int type in the ToolBar class. This is done to resolve the problem of keeping the line tool active even without double-clicking on it. A tool may be on (active) after a click on it. Its active status determines the next action. However, after the action is done, the fixed tool becomes active. A tool becomes fixed after a double-click on it.
Code 06-07.19: The ToolBar class with private onTool and fixedTool attributes.
class ToolBar {
…
int _onTool;
int _fixedTool;
…
ToolBar(this.board) {
…
selectButton.onDoubleClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
onTool(SELECT);
_fixedTool = SELECT;
});
…
boxButton.onDoubleClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
onTool(BOX);
_fixedTool = BOX;
});
…
lineButton.onDoubleClick.listen((MouseEvent e) {
onTool(LINE);
_fixedTool = LINE;
});
onTool(SELECT);
_fixedTool = SELECT;
}
…
void backToFixedTool() {
onTool(_fixedTool);
}
void backToSelectAsFixedTool() {
onTool(SELECT);
_fixedTool = SELECT;
}
}After a selection of boxes and lines is deleted, a diagram may be empty. In that case the fixed tool must return to select.
Code 06-07.20: When deleting a selection of all boxes and lines.
void deleteSelection() {
deleteSelectedLines();
deleteSelectedBoxes();
if (isEmpty()) {
toolBar.backToSelectAsFixedTool();
}
}
bool isEmpty() {
if (boxes.length == 0 && lines.length == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}The private boxExists method of the Board class returns true if the given box is a member of the boxes attribute.
Code 06-07.21: The private boxExists method of the Board class.
bool _boxExists(Box box) {
for (Box b in boxes) {
if (b == box) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}This method is called in the onMouseDown method to check if the last two boxes clicked used in a new line creation do actually exist. After one of actions is done by the onMouseDown method, the fixed tool is back.
Code 06-07.22: The onMouseDown method of the Board class.
void onMouseDown(MouseEvent e) {
bool clickedOnBox = false;
for (Box box in boxes) {
if (box.contains(e.offset.x, e.offset.y)) {
// Clicked on the existing box.
clickedOnBox = true;
break;
}
}
if (!clickedOnBox) {
if (toolBar.isSelectToolOn()) {
Point clickedPoint = new Point(e.offset.x, e.offset.y);
Line line = _lineContains(clickedPoint);
if (line != null) {
// Select or deselect the existing line.
line.toggleSelection();
} else {
// Deselect all.
deselect();
}
} else if (toolBar.isBoxToolOn()) {
// Create a box in the position of the mouse click on the board.
Box box = new Box(this, e.offset.x, e.offset.y, Box.DEFAULT_WIDTH, Box.DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
if (e.offset.x + box.width > width) {
box.x = width - box.width - 1;
}
if (e.offset.y + box.height > height) {
box.y = height - box.height - 1;
}
boxes.add(box);
} else if (toolBar.isLineToolOn()) {
// Create a line between the last two clicked boxes.
if (beforeLastBoxClicked != null && lastBoxClicked != null &&
_boxExists(beforeLastBoxClicked) && _boxExists(lastBoxClicked)) {
Line line = new Line(this, beforeLastBoxClicked, lastBoxClicked);
lines.add(line);
}
}
toolBar.backToFixedTool();
}
}In the onMouseDown method of the Box class, when a box is clicked on, before it becomes the last box clicked, the actual last box clicked first becomes the box clicked before the last one, but only if it is not null and if it is different from the current box.
Code 06-07.23: Updating the two last boxes clicked.
void onMouseDown(MouseEvent e) {
_mouseDown = true;
if (board.toolBar.isSelectToolOn() && contains(e.offset.x, e.offset.y)) {
toggleSelection();
}
if (contains(e.offset.x, e.offset.y)) {
if (board.lastBoxClicked != null && board.lastBoxClicked != this) {
board.beforeLastBoxClicked = board.lastBoxClicked;
}
board.lastBoxClicked = this;
}
}